Lecture 32: Single-Server Queueing Systems in Python#
Note
This lecture details how to simulate a single-server queueing system developing the simulation logic along with its implemenation in Python
Simulation Logic#
Procedure \(\text{SSQ}(n,A,S)\)
// SYSTEM STATUS
\(t \ \leftarrow 0\) // simulation clock
\(\varphi \leftarrow 0\) // server idle/busy
\(Q \leftarrow \varnothing\) // queue
// SYSTEM DYNAMICS
\(T_a \leftarrow \{\}\) // customer arrival time
\(T_s \leftarrow \{\}\) // customer service initiation time
\(T_d \leftarrow \{\}\) // customer departure time
// SYSTEM LOG
\(T_o \leftarrow \{\}\) // event time (arrival/service initiation/departure)
\(\Phi \leftarrow \{\}\) // server status at event time
\(J \leftarrow \{\}\) // queue length at event time
// INITIALIZATION
\(i \ \leftarrow 0\) // index of last customer serviced
\(j \ \leftarrow 0\) // queue length
\(k \leftarrow 0\) // customers serviced
\(t_a \leftarrow A_i\) // next arrival event time
\(t_d \leftarrow A_i + S_i\) // next departure event time
while \(k < n\) do
if \(t_a \leq t_d\) then // time jump to next customer arrival event
\(e \leftarrow 1\)
\(t \leftarrow t_a\)
else // time jump to next customer departure event
\(e \leftarrow -1\)
\(t \leftarrow t_d\)
end if
if \(e = 1\) then // update system status for customer arrival
\(T_o \leftarrow T_o \cup \{t\}\)
\(T_a \leftarrow T_a \cup \{t\}\)
if \(\varphi = 0\) then
\(e \leftarrow 0\)
\(i \leftarrow i + 1\)
else
\(Q \leftarrow Q \cup \{i+j+1\}\)
\(j \leftarrow j + 1\)
end if
\(t_a \leftarrow (i+j+1 \leq n) \ ? \ t + A_{i+j+1} : \infty\)
\(\Phi \leftarrow \Phi \cup \{\varphi\}\)
\(J \leftarrow J \cup \{j\}\)
else if \(e = -1\) then // update system status for customer departure
\(T_o \leftarrow T_o \cup \{t\}\)
\(T_d \leftarrow T_d \cup \{t\}\)
if \(j = 0\) then
\(\varphi \leftarrow 0\)
\(t_d \leftarrow= \infty\)
else
\(e \leftarrow 0\)
\(i \leftarrow \text{pop}(Q)\)
\(j \leftarrow j - 1\)
end if
\(\Phi \leftarrow \Phi \cup \{\varphi\}\)
\(J \leftarrow J \cup \{j\}\)
\(k \leftarrow k + 1\)
end if
if \(e = 0\) then // update system status for customer service intiation
\(T_o \leftarrow T_o \cup \{t\}\)
\(T_s \leftarrow T_s \cup \{t\}\)
\(\varphi \leftarrow 1\)
\(t_d \leftarrow t + S_i\)
\(\Phi \leftarrow \Phi \cup \{\varphi\}\)
\(J \leftarrow J \cup \{j\}\)
end if
end while
\(d \leftarrow \sum_{i=1}^{n}(T_{s_i} - T_{a_i}) / n\) // average delay
\(q \leftarrow \) // average queue length
\(u \leftarrow \Phi \cdot T_o / t\) // average utilization
return d, q, u
Implementation#
def ssq(n, A, S, silent=False):
"""
This function simulates a single-server queueing system for n customers given their inter-arrival times - A, and service times - S
Parameters
---
n: int
number of customers
A: list[float]
customer inter-arrival times
S: list[float]
customer service times
silent=False: bool
run in silence if True else display system
Returns
---
d: float
average delay
q: float
average queue length
u: float
average utilization
"""
# System Status
t = 0 # simulation clock
z = 0 # server status
Q = [] # queue
# System Dynamics
Ta = [] # customer arrival time
Ts = [] # customer service initiation time
Td = [] # customer depature time
# System Log
To = [0] # event time (customer arrival/service initiation/departure time)
Z = [0] # server status at event time
J = [0] # queue length at event time
# Initialization
i = -1 # index of last customer serviced
j = 0 # queue length
k = 0 # customers serviced
ta = A[0] # next arrival event time
td = A[0] + S[0] # next departure event time
# Loop
while k < n:
if ta <= td: # time jump to next customer arrival event
e = 1
t = ta
else: # time jump to next customer departure event
e = -1
t = td
if e == 1: # update system status for customer arrival
To.append(t)
Ta.append(t)
if z == 0:
e = 0
i = i + 1
else:
Q.append(i+j+1)
j = j + 1
ta = round(ta + A[i+j+1], 1) if i+j+1 < len(A) else float('inf')
Z.append(z)
J.append(j)
if not silent: print("Arrival : ", " ", "X", i , Q)
elif e == -1: # update system status for customer departure
if not silent: print("Departure : ", i, "X", " ", Q)
To.append(t)
Td.append(t)
if j == 0:
z = 0
td = float('inf')
else:
e = 0
i = Q.pop(0)
j = j - 1
Z.append(z)
J.append(j)
k = k + 1
if e == 0: # update system status for customer service initiation
To.append(t)
Ts.append(t)
z = 1
td = t + S[i]
Z.append(z)
J.append(j)
if not silent: print("Service : ", " ", "X", i, Q)
T = [To[i]-To[i-1] for i in range(1,len(To))] + [0.0]
d = round(sum([Ts[i] - Ta[i] for i in range(n)]) / n, 3) # average delay
q = round(sum([J[i] * T[i] for i in range(len(T))]) / t, 3) # average queue length
u = round(sum([Z[i] * T[i] for i in range(len(T))]) / t, 3) # average utilization
return d, q, u
# Single Simulation Outcomes
n = 6
A = [0.4, 1.2, 0.5, 1.7, 0.2, 1.6, 0.2, 1.4, 1.9]
S = [2.0, 0.7, 0.2, 1.1, 3.7, 0.6, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
ssq(n, A, S)
Arrival : X 0 []
Service : X 0 []
Arrival : X 0 [1]
Arrival : X 0 [1, 2]
Departure : 0 X [1, 2]
Service : X 1 [2]
Departure : 1 X [2]
Service : X 2 []
Departure : 2 X []
Arrival : X 3 []
Service : X 3 []
Arrival : X 3 [4]
Departure : 3 X [4]
Service : X 4 []
Arrival : X 4 [5]
Arrival : X 4 [5, 6]
Arrival : X 4 [5, 6, 7]
Departure : 4 X [5, 6, 7]
Service : X 5 [6, 7]
Arrival : X 5 [6, 7, 8]
Departure : 5 X [6, 7, 8]
Service : X 6 [7, 8]
(0.95, 1.217, 0.902)
import random
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def simulate(sims=1000, n=100, lam=0.8, mu=1.0):
"""
Run Monte Carlo simulation of SSQ using exponential inter-arrivals and service times.
Parameters
----------
sims : int
number of simulations (default=1000)
n : int
number of customers per run (default=100)
lam : float
arrival rate λ
mu : float
service rate μ
Returns
-------
df : pandas.DataFrame
Results with columns ['d','q','u']
"""
# Random simulations
results = []
for k in range(sims):
rng = random.Random(k)
# Generate n+5 to avoid indexing issues in ssq
A = [rng.expovariate(lam) for _ in range(n+5)]
S = [rng.expovariate(mu) for _ in range(n+5)]
d, q, u = ssq(n, A, S, silent=True)
results.append((d, q, u))
return pd.DataFrame(results, columns=["d","q","u"])
# Descriptive statistics
def describe_series(x: pd.Series):
arr = np.asarray(x, dtype=float)
mean = float(np.mean(arr))
median = float(np.median(arr))
rng = float(np.max(arr) - np.min(arr))
sd = float(np.std(arr, ddof=1))
iqr = np.percentile(arr, 75) - np.percentile(arr, 25)
skew = np.mean((arr - mean)**3) / (sd**3) if sd > 0 else np.nan
kurt = np.mean((arr - mean)**4) / (sd**4) - 3 if sd > 0 else np.nan
return {
"mean": mean, "median": median, "range": rng,
"sd": sd, "iqr": iqr, "skewness": skew, "kurtosis": kurt
}
def summarize_df(df: pd.DataFrame):
return pd.DataFrame({col: describe_series(df[col]) for col in df.columns}).T
# Run and visualize
if __name__ == "__main__":
df = simulate(sims=1000, n=1000, lam=0.8, mu=1.0)
summary = summarize_df(df).round(4)
print("\nSummary Statistics (1000 runs, n=100)\n")
print(summary.to_string())
print("\nNote: kurtosis is excess kurtosis.\n")
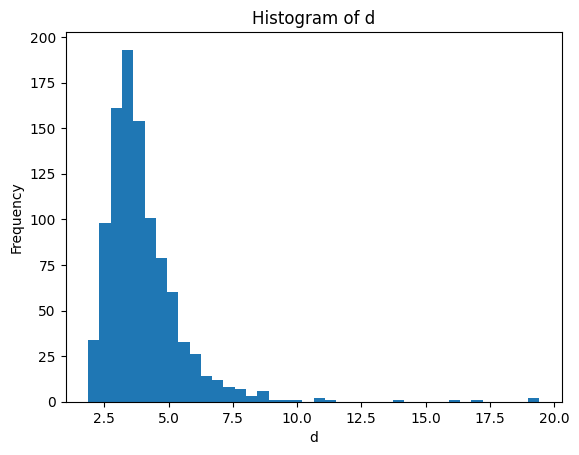
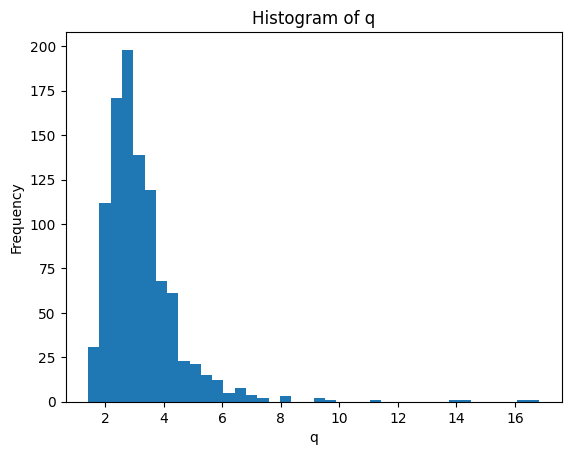
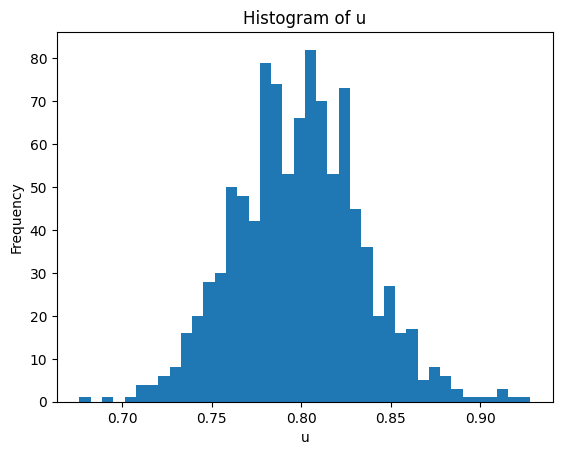
# Histograms
for metric in ["d","q","u"]:
plt.figure()
plt.hist(df[metric], bins=40)
plt.title(f"Histogram of {metric}")
plt.xlabel(metric)
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.show()
Summary Statistics (1000 runs, n=100)
mean median range sd iqr skewness kurtosis
d 4.0092 3.6670 17.552 1.6074 1.4693 3.6866 25.0216
q 3.2290 2.9295 15.411 1.3720 1.2185 3.8767 27.4364
u 0.7985 0.7980 0.252 0.0352 0.0470 0.1558 0.2841
Note: kurtosis is excess kurtosis.